Home networking, while mostly straightforward, is not without its technical jargon, hiccups, and nuance. I’ve definitely hit a few stumbling block along the way, and I want to make your experience as painless as possible. One question that comes up often is: do routers have IP addresses? Let’s dive in and find out.
Routers have two types of IP addresses: a public IP address for the router, and private IP addresses for the router and for every device connected to it.
This may seem confusing at first, but I’ll walk you through the whole thing so you don’t have the same frustrations I had setting up my home network.

What is an IP address?
The IP in IP address stands for Internet Protocol, and IP addresses are unique numbers assigned to a router or device so that other devices can find it on the internet. Because IP addresses are unique and all online devices have IP addresses, devices connected to the internet are easy to identify and it’s simple to exchange data between those devices.
For the sake of simplicity, we’ll stick with IPv4 IP addresses today because they’re the most common type of IP address in use today. While IPv6 IP addresses exist, we won’t get into that today as they are not nearly as common.
As previously stated, IP addresses are numbers, and they commonly look something like this: 192.168.28.151. Further, there are a few rules that govern IP addresses:
- There are four sets of numbers, and periods separate the number sets.
- Numbers can be 1,2, or 3 digits.
- The range of numbers used in an IP address go from 0 to 255. Therefore, IP addresses range from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255.
- The IP address must be unique.
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority governs the use of IP addresses; check out their website for more information. The IANA is a subsidiary of the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers.
What are the two types of IP addresses for my router?
The two types of IP addresses used by your router are public IP addresses and private IP addresses. Each type serves a different purpose. Let’s break down the specifics of the two types router IP addresses.
We’ll get into more detail later, but here’s a quick chart about the differences between public and private IP addresses:
| Type of IP Address | Who assigns the IP address? | Public or Private | Main Use | Also called |
| Public IP Address | Internet Service Provider | Public – other networks and computers can see it. | Interacting with other computers and networks on the internet. | WAN (Wide Area Network) IP, External IP. |
| Private IP Address | Router | Private – for use only on the local network. | Each device on the network gets a private IP address so the router can send internet traffic to the right device. | LAN (Local Area Network) IP, Internal IP. |
1. Public Router IP address
Your ISP assigns your router a public IP address, and your router uses that unique IP address to interact with all the other computers on the internet. ISP stands for Internet Service Provider, and they are the company you pay every month for your internet access. Well-known ISPs in the U.S. include Comcast, MediaCom, Charter, and CenturyLink. Routers use public IP addresses to send and receive information to computers outside your network.
The two types of Public IP addresses
There are two different types of public IP addresses for your router, and your router can only have one kind.
1. Dynamic Public IP address
A dynamic public IP address for a router is one that changes over time. Your ISP assigns public IP addresses, and you won’t notice when your ISP changes your dynamic public IP address. Most likely, your ISP changed your public IP address many times and you were none the wiser.
ISPs purchase large volumes of IP addresses, and they then cycle them to customers as they see fit. There are two main benefits to dynamic public IP addresses:
- Dynamic public IP addresses are harder to hack. The simple fact is that moving targets are harder to hit than stationary targets. As your public IP address changes, it becomes harder for hackers to get into your network.
- Dynamic public IP addresses are cheaper for the ISP. ISPs purchase large volumes of IP addresses to hand out to customers, and dynamic IP addresses ensure that they don’t have to waste IP addresses on people who disconnect service, move, or otherwise no longer need the IP address. Further, IP addresses can be reused by different customers over time.
2. Static Public IP addresses
Static IP addresses are IP addresses that remain constant. Theses are common with businesses who use their own server or have a specific need on their network for an IP address that remains constant.
Generally speaking, you need to request a static IP address from your ISP and pay them an additional fee.
Do all routers have public IP addresses?
All routers have public IP addresses.
How do I find my router’s my public IP address?
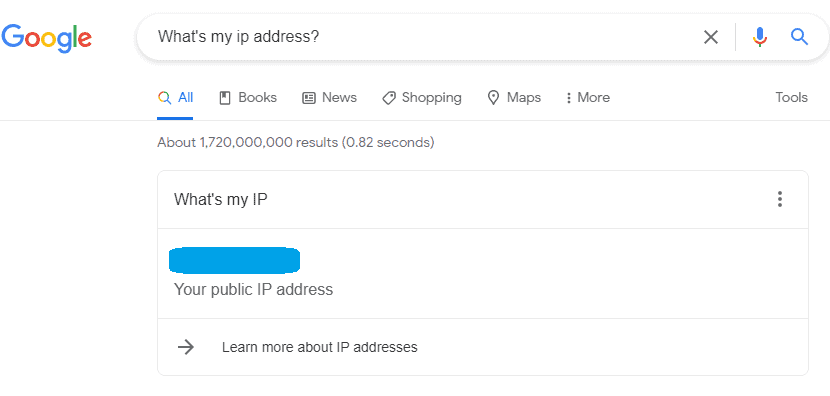
The easiest way to find your router’s public IP address is to perform a Google search for What’s my IP address?
After your search, Google will show you your public IP address. For obvious reasons, I obscured my IP address.
2. Private Router IP Address
Your router assigns itself and all of the devices connected to it a private IP address, and it these IP addresses are for use only on one network. The router’s public and private IP addresses are different from one another.
Every device on a network has its own unique private IP address for use only on that network. Devices that connect to many networks (such as laptops) receive a new private IP address from each router with which they’ve made a connection for use on that individual network.
Private IP addresses are only used on the local network between the individual device and the router. Therefore, there’s no danger in multiple routers using identical private IP addresses on different networks; this explains why many private IP addresses commonly use the format 192.168.xxx.xxx.
Only the router’s public IP address accesses the internet.
What can I do with my router’s private IP address?
Typing your router’s private IP address into any web browser (Chrome, Edge, Firefox, etc.) enables you to log-in to your router’s software, change settings, and see all of the devices connected to your network.
How do I find my router’s private IP address?
Finding your router’s private IP address is fairly straightforward, but it varies based on your device’s Operating System.
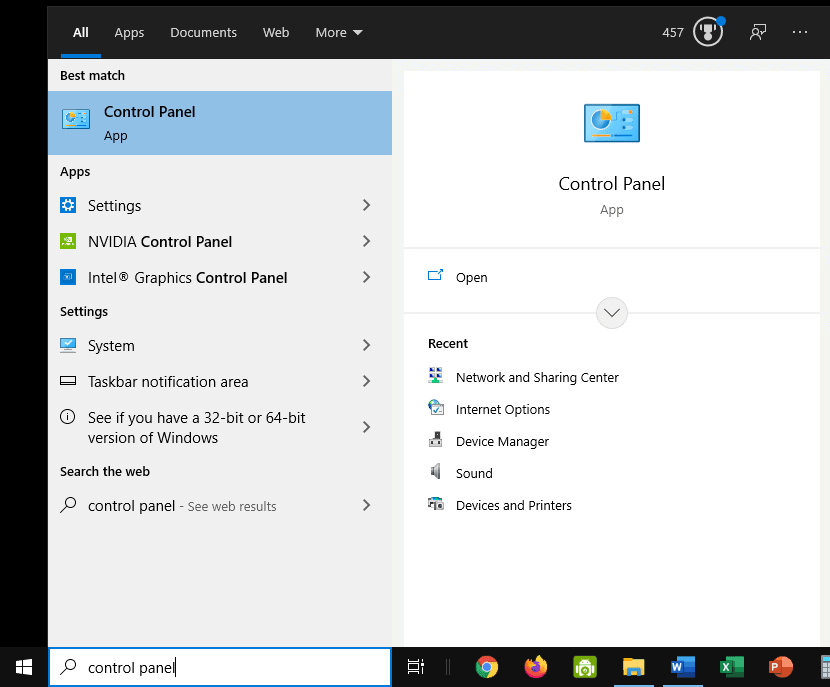
How to find your router’s private IP address in Windows 10 using the Control Panel app
Most people are familiar with Windows’ Control Panel, and I thought it would be a good place to start learning how to find your router’s private IP address.
- Go to the Search box in the lower left corner of your screen, type: Control Panel, and then choose the Control Panel app.
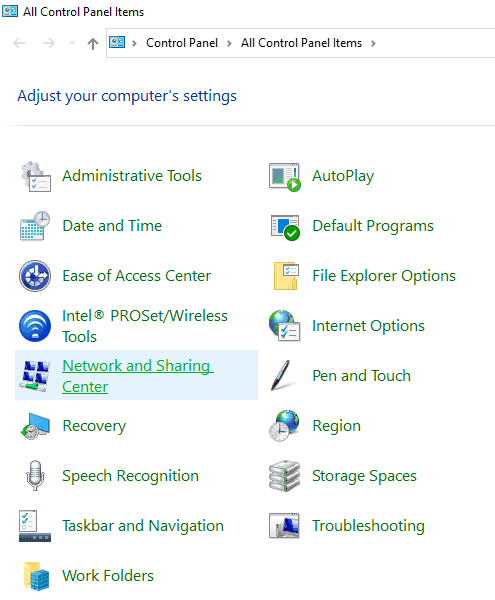
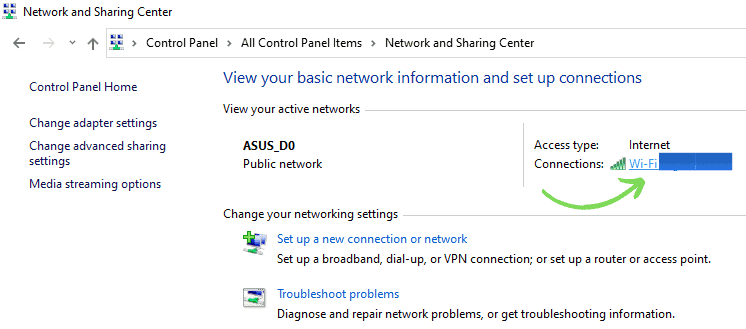
- Click on Network and Sharing Center.
- Select Wi-Fi (SSD).
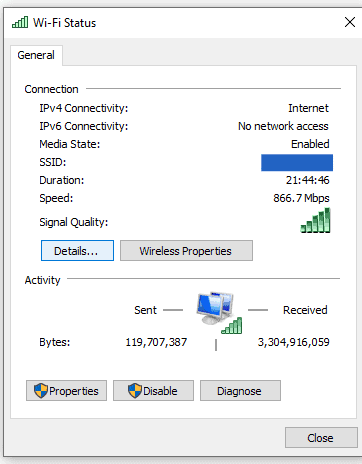
- Click on Details.
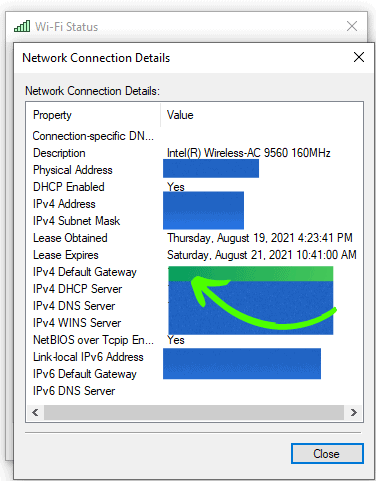
- Your private IP address is listed as the IPv4 Default Gateway.
How to find your router’s private IP address in Windows 10 using Command Prompt
Another easy way to find your router’s private IP address on Windows 10 is to use the Command Prompt app, and I’ll walk you through it below.
- Go to the Search box in the lower left corner of your screen, type: Command Prompt, and then choose the Command Prompt App.
- After the Command Prompt App opens, type in ipconfig and press Enter.
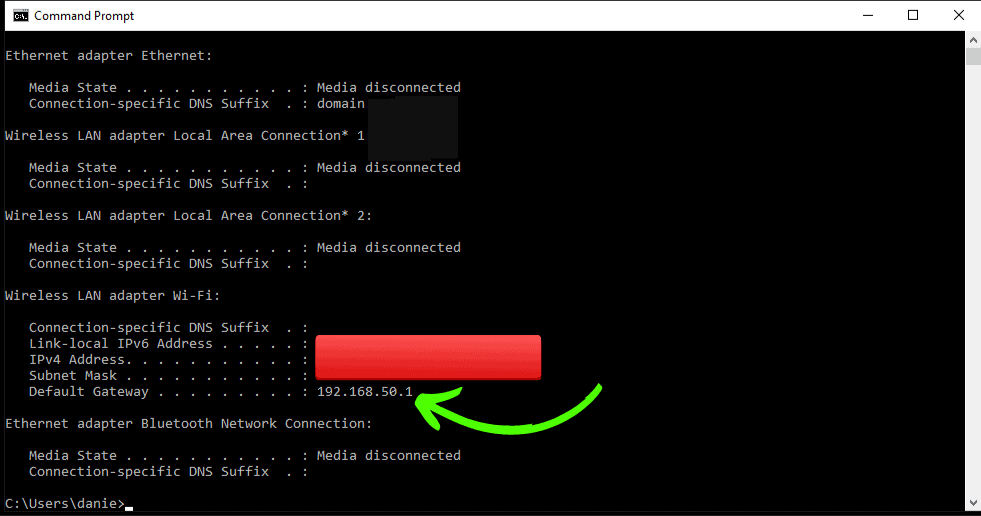
- Your screen will look something like the image below, and your router’s private IP address is listed as the Default Gateway.
How to find your router’s private IP address on Mac
Finding your router’s private IP address on a Mac is pretty simple, and I’ll walk you through it below.
- Go to your Utilities folder.
- Open the Terminal app.
- Type: netstat -nr|grep default and then press Return.
- Your Private IP address is listed next to the text default.
What about the devices connected to my network that aren’t the router?
The router assigns each device on the network its own unique private IP address, and then the router manages all incoming and outgoing internet traffic on the network.
The best way to find out the private IP address of an individual device connected to your network is to log-in to your router’s software. You can do this by entering your router’s private IP address (as found in the previous steps) into the address bar of a web browser and pressing Enter.
The default login credentials for a router are commonly printed on a label on the router. This will only work if you haven’t updated the credentials.
How do public and private IP addresses work together?
A simple way to think of it is that your router is the gatekeeper of internet traffic for your home. Here’s a simplified overview of how public and private IP addresses work on a home network assuming everything is already connected.
- A laptop connected to the local Wi-Fi router opens a web browser and does a search for Alligators.
- Because the laptop is already connected and the router already assigned it a private IP address, the router knows exactly which laptop to send the data back to.
- The router sends a request to the search engine using the router’s public IP address. The search engine has absolutely no idea which device on the network requested the info; it just knows which router requested in the data.
- The search engine then sends the requested data back to the router’s public IP address.
- The router knows that the laptop requested information about alligators; it then sends the information back to the laptop using the laptop’s private IP address.
That’s basically how it works. One of the main jobs of the router is to switch data from private to public using the appropriate IP address.
Final Thoughts
Do routers have IP addresses? Not only do routers have IP addresses, they have two types: public and private. Both types of IP addresses work together to make home networks work. I certainly hope I provided some helpful information.
Take care!
If you’re interested in reading more about Wi-Fi and how it works, check out my article, Does Wi-Fi Go Through Walls? In this article, we discuss building material, Wi-Fi signals, and
